Newsletter
Newsletter  Toshiba Lithium-Ion Battery “SCiB™’’ Powering India's Sustainable Leap
Toshiba Lithium-Ion Battery “SCiB™’’ Powering India's Sustainable Leap
Toshiba Lithium-Ion Battery “SCiB™’’ Powering India's Sustainable Leap

India’s Green Shift: A Rising Demand for Advanced Energy and Mobility Solutions
India is undergoing a sweeping transformation in its energy and mobility landscape, driven by ambitious government initiatives and an urgent response to climate change. Programs like FAME II (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles), the National Electric Mobility Mission, and the PM Gati Shakti, a national master plan to boost infrastructure, are accelerating the transition to clean transportation with induction of electric buses in public intra-city transport infrastructure and at airports.
Simultaneously, India’s maritime sector is witnessing the early adoption of electric and hybrid vessels. Initiatives under the Sagarmala Project and Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways are promoting the electrification of ferries and port operations. The Green Tug Transition Program (GTTP), part of the broader ‘Panch Karma Sankalp’, is targeting a complete shift to green tugs at Indian Major Ports by 2040.
On the energy front, India’s commitment to 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030 is heavily reliant on large-scale Energy Storage Systems (ESS). As renewable energy capacity rises, storage is essential to managing intermittency and grid stability. The country will require at least 160 GWh of battery storage by 2030.
Powering Through Extreme, Need for Safer, More Resilient Battery Solutions
India’s transition to clean mobility and energy is not without its hurdles—chief among them are the country’s extreme climatic conditions and demanding usage patterns. In many regions, surface temperatures can exceed 45°C during peak summer months, subjecting battery systems to severe thermal stress. When paired with high-utilization scenarios—such as electric buses in continuous urban transit, airport ground fleets operating round-the-clock, and hybrid marine vessels navigating rough coastal conditions—conventional lithium-ion batteries are often pushed beyond their optimal charge and discharge limits. This can accelerate performance degradation, reduce battery life, and, more critically, increase safety risks like thermal runaway and fire hazards. These concerns are especially pressing in sectors where uptime, reliability, and safety are paramount, underscoring the urgent need for battery technologies that are purpose-built for India’s intense operating environments.
Engineered for India: Toshiba Lithium-Ion Battery “SCiB™’’ Powering India’s Energy and Mobility Future
India’s high temperatures, intensive usage cycles, and demand for long-term operational reliability pose significant challenges to conventional battery technologies. These harsh conditions increase the risk of thermal stress, performance degradation, and safety incidents—especially in sectors like electric mobility and energy storage where uptime and safety are critical. SCiB™ lithium-ion battery by Toshiba directly addresses these challenges. Leveraging Lithium Titanium Oxide (LTO) chemistry, SCiB™ stands out with its fast charging and discharging capabilities, a long life of over 20,000 cycles, and outstanding thermal and chemical stability. These features make it exceptionally reliable in India’s diverse and extreme environments—from scorching heat to high-vibration and high-demand scenarios. By addressing the risk of overheating and fires while delivering consistent performance over years, SCiB™ not only improves operational safety but also lowers total lifecycle costs—making it an ideal choice for scalable, dependable clean energy and mobility solutions across the country.
Empowering India’s Electric Buses
India’s electric bus market is expanding rapidly, driven by the government’s efforts to reduce emissions and pollution in urban areas. As part of the FAME II program, electric buses are gaining significant traction, with over 6,800 e-buses already sanctioned and more than 5,000 already deployed to various cities under the FAME-II Scheme. With the PM e-Bus Sewa-Payment Security Mechanism (PSM) Scheme, deployment of more than 38,000 electric buses across Indian cities will be supported. Airports are also leading the way in electric bus adoption, replacing their traditionally diesel-powered airside buses with electric models. For instance, airports in Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad are integrating electric buses into their fleets as part of a broader sustainability initiative. Electric buses at airports need batteries that provide rapid charging and a long lifespan to keep operations running smoothly, while maintaining safety even under extreme temperature conditions.
Toshiba lithium-ion battery SCiB™ is uniquely suited to meet these requirements, providing a reliable and efficient power source for electric buses operating in demanding environments. SCiB™ quick charge/discharge cycles (charge from 0 to 80% in 6 minutes at cell level), long life cycle (over 20,000 charge and discharge cycles), and thermal stability make it an ideal choice for powering India’s growing fleet of electric buses.
Transforming India's Maritime Sector
India’s maritime sector is also undergoing a green revolution. The Sagarmala Project, which aims to modernize India’s ports and waterways, includes plans for electrifying maritime transport. India's inland and coastal waterways are embracing electrification, with projects like the Kochi Water Metro aiming to deploy 78 battery-powered boats across 38 terminals, serving up to 150,000 daily commuters. Kerala has operational electric ferries in its backwaters, and Assam is deploying them along the Brahmaputra. Meanwhile, hybrid and electric tugboats are being explored at ports like Chennai and Mumbai, as India aims to modernize and decarbonize maritime logistics. In addition, the GTTP under the ‘Panch Karma Sankalp’ is designed to phase out conventional fuel-based harbour tugs operating in Indian major ports and replace them with green tugs powered by cleaner and more sustainable alternate fuels by the end of 2040, ensuring a standardized, eco-friendly fleet across the country.
In order to address these requirements, electric vessels and hybrid ships necessitate batteries that prioritize safety to protect the lives of individuals on board during operation, as well as the ability to sustain high charge and discharge performance with long life cycles in vibration-heavy environments, and perform under variable weather conditions. Toshiba lithium-ion battery SCiB™ technology, with its enhanced low internal resistance, resulting in less heat dissipation, is well-positioned to power these electric ships, ensuring reliable and safe operations in India's waterways.
Advancing Energy Storage Systems
With India’s rapid adoption of renewable energy, particularly solar and wind, there is a growing need for Energy Storage Systems (ESS) to manage energy intermittency and ensure grid stability To support the integration of renewable energy into the grid and ensure reliable power supply, India will require at least 160 GWh of battery storage by 2030. Additionally, the Ministry of Power has announced a Viability Gap Funding (VGF) scheme for 4,000 MWh of battery energy storage projects, highlighting the government’s commitment to incentivizing ESS infrastructure. States like Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu are leading the way by floating tenders for both front-of-the-meter and behind-the-meter storage systems.
Toshiba lithium-ion battery SCiB™ offers rapid charge/discharge capabilities and long lifespan, making it an ideal choice for ESS applications, contributing to grid stability and efficient energy management. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and provide consistent performance over 20,000 charge cycles make it an ideal choice for both grid stabilization and off-grid storage, which is critical in India’s quest for a sustainable energy future.
Toshiba Lithium-Ion Battery SCiB™: All-Terrain Battery for India's Clean Energy & Mobility Transformation
Toshiba lithium-ion battery SCiB™ technology is redefining clean energy and mobility in India by delivering unmatched safety, performance, and adaptability. Addressing India’s diverse and demanding conditions, SCiB™ is ideal for both mobile applications-including electric buses, commercial fleets, and marine vessels and stationary systems like Energy Storage Solutions (ESS) that are crucial to renewable energy integration and grid resilience. Its robust design ensures reliable operation across urban, rural, and industrial environments, making it a foundational technology for India's sustainable future. It offers:
- Long Cycle Life: With a lifespan exceeding 20,000 charge cycles, SCiB™ significantly reduces replacement frequency and long-term costs-perfect for high-use cases such as public transport and utility-scale ESS.
- Fast Charging: From 0 to 80% in just six minutes, minimizing downtime for electric buses, hybrid vessels, offshore power systems, and high-turnover commercial fleets. This ensures greater operational efficiency without sacrificing battery health.
- Thermal Safety: Engineered to prevent thermal runaway, SCiB™ prevents thermal runaway due to internal short circuit conditions and hence preventing the fire risk situation where conventional lithium-ion batteries may be hazardous under similar conditions.
- High Vibration Resistance: Built to withstand mechanical stress, SCiB™ at module level is ideally suited for marine and transport environments with continuous motion, like electric ferries, tugboats and buses.
Together, these features make Toshiba lithium-ion battery SCiB™ product for cleaner, smarter energy and mobility goals.
New Technology, especially for India’s Extreme Climate
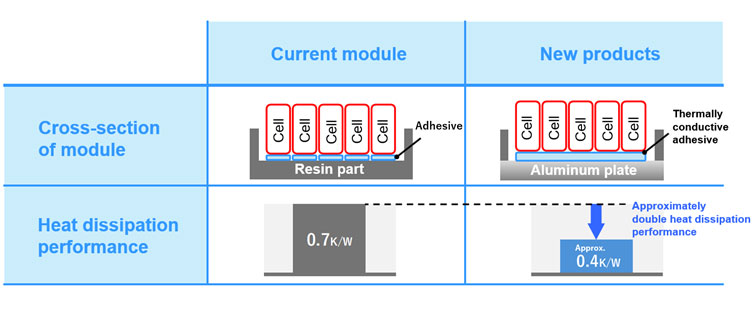
In April 2025, Toshiba Corporation launched a new SCiB™ module, a lithium-ion battery designed for use in EV buses, electric ships, and stationary applications. The new product features an aluminium baseplate that dissipates approximately twice the heat of current modules and delivers a balance between constant high input and output in a short time and battery life. The battery module will be certified under the UL1973 safety standard for stationary applications, including off-grid applications and microgrids. Designed to meet diverse customer requirements, Toshiba aims to meet this increasing for various applications, including hybrid vehicles and industrial equipment.

Enhanced heat dissipation with aluminum baseplate
The Way Forward
As India accelerates its transition towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient future, the role of innovative technologies like Toshiba’s lithium-ion battery SCiB™ becomes increasingly pivotal. With its superior heat dissipation, rapid charging capabilities, long cycle life, and exceptional safety & performance characteristics in extreme conditions, SCiB™ is poised to support India’s evolving needs in electric mobility, maritime transport, and energy storage systems. Toshiba’s ongoing commitment to innovation ensures that the company will continue to provide cutting-edge solutions, empowering industries to meet their sustainability goals.
Adding new products to its module lineup allows Toshiba to respond flexibly to customer demands and application requirements. Toshiba will continue to offer products that leverage the unique features of its SCiB™ lithium-ion battery, while fully considering customer lifecycle costs, from installation to maintenance and disposal.